How to Check User Roles in SQL Server
Native Solution vs. Netwrix Auditor for SQL Server
Netwrix Auditor for SQL Server
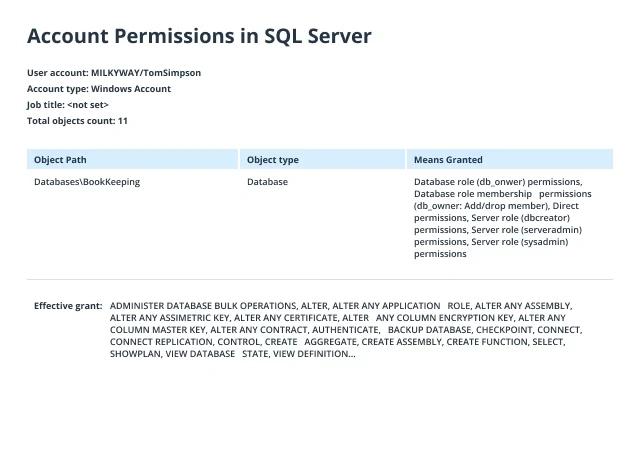
- Open Netwrix Auditor and navigate to Reports -> Predefined -> SQL Server - State-in-Time -> Account Permissions in SQL Server.
- Specify the following filters:
- In the User account filter, type the full user name (such as MILKYWAY/TomSimpson).
- In the Object type filter, choose Server Instance, Database.
- Click View to create a clear report on the effective permissions for the user.
Native Solution
Listing SQL Server roles for a user
- Start Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (MSSMS).
- On the File menu, click Connect Object Explorer.
- In the Connect to Server dialog box, specify the following settings:
- In the Server type list box, select Database Engine.
- In the Server name text box, type the name of the SQL cluster server.
- In the Authentication list box, choose your SQL Server Authenticationmethod and specify the credentials to use. If you do not want to re-type the password whenever you connect to the server, tick Remember password.
- Click Connect.
- Click Execute (or hit the F5 key).
- Upon connection, click New Query and paste the following script into the query field:
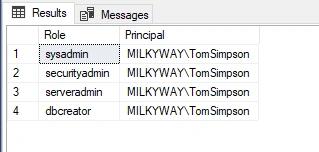
select r.name as Role, m.name as Principal
from
master.sys.server_role_members rm
inner join
master.sys.server_principals r on r.principal_id = rm.role_principal_id and r.type = 'R'
inner join
master.sys.server_principals m on m.principal_id = rm.member_principal_id
where m.name = 'MILKYWAY\TomSimpson'
- Review the list of server-level roles and principals (member names) in the query execution results:
Querying database roles in SQL Server for a user
- Start Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio (MSSMS).
- On the File menu, click Connect Object Explorer.
- In the Connect to Server dialog box, specify the following settings:
- In the Server type list box, selectDatabase Engine.
- In the Server name text box, type the name of the SQL cluster server.
- In the Authentication list box, choose your SQL Server Authentication method and specify the credentials to use. If you do not want to re-type the password whenever you connect to the server, tick Remember password.
- Click Connect.
- Click Execute (or hit the F5 key).
- Upon connection, select the Database you need to query for user roles.
- Click New Query and paste the following script into the query field:
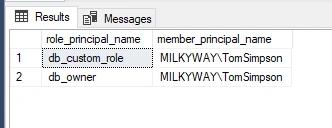
SELECT r.name role_principal_name, m.name AS member_principal_name
FROM sys.database_role_members rm
JOIN sys.database_principals r
ON rm.role_principal_id = r.principal_id
JOIN sys.database_principals m
ON rm.member_principal_id = m.principal_id
where m.name = 'MILKYWAY\TomSimpson'
- Review the list of server-level roles and principals (member names) in the query execution results:
Discover how to check user roles in SQL Server without a single query.
Microsoft SQL Server provides roles to help database administrators manage permissions to structured data. Server-level roles, as their name implies, grant access server-wide, similar to groups in the Windows world. Each SQL database can also have its unique permissions and roles.
To maintain security and comply with many regulations, including PCI DSS and HIPAA, you need to know all the server and database roles assigned to each user. Because of the complexity involved, that’s a tough job if all you have are native tools.
To start with, server-level settings, such as server roles, permissions, user credentials, and dependencies, are stored in the master database. Using the sys.server_principals system view.,
- To list users and server roles in SQL Server, you can query system views like sys.server_principals.
- To list users and roles for databases in SQL Server, you can query system views like sys.database_principals.
While stored procedures can assist you in managing areas of the server, you will have to use queries to build custom reports (for example, one that matches several tables by specific column names). For instance, server-level role membership info is stored in the server_role_members system view of the master database. Since principals’ IDs are linked, you can get a summary of SQL Server user roles with a query by joining sys.server_principals with master.sys.server_role_members based on ID number. Although users can view their server role membership and the principal ID of each member of the fixed server roles, remember that viewing all server role membership requires additional permissions or membership in the security admin fixed server role.
To gather database-level information, you must query SQL Server database roles on each database individually, which can be time-consuming. Moreover, roles can be nested: Database users, application roles, and other database roles can be members of a database role.
In short, getting comprehensive information on current user roles with native tools can be complicated and downright exhausting. With Netwrix Auditor, on the other hand, you can get detailed information on who holds which server and database roles in a readable format in a few clicks. The linked reports included in the product enable your specialists to quickly sift through the complications of nested user role membership across an entire server, streamlining investigations. You get all the critical details you need: a list of every object the user has access to, with its path and object type, the permissions that were granted, how they were granted (directly, through role membership, etc.), and whether they are explicit or inherited. You can analyze permissions from different angles, including the account, object, and server levels. All this information is presented and available without the hassle of writing scripts, exporting information into Excel, and manually sifting through it.
Share on
